Milvus 是一個開源的向量數(shù)據(jù)庫,專為管理和檢索大量向量數(shù)據(jù)而設(shè)計,廣泛應(yīng)用于人工智能、推薦系統(tǒng)、圖像檢索、自然語言處理等領(lǐng)域。它支持 PB 級別的數(shù)據(jù)存儲,提供高性能的向量檢索服務(wù)。
Milvus 的核心功能
1. 高效檢索: 支持 ANN(近似最近鄰)檢索,適用于超大規(guī)模向量檢索任務(wù)。
2. 多數(shù)據(jù)類型: 支持文本、圖像、視頻等多種嵌入向量數(shù)據(jù)。
3. 彈性擴展: 支持水平擴展和分布式部署。
4. 多種索引類型: 包括 IVF、HNSW、DiskANN 等。
5. 多語言 SDK 支持: 提供 Python、Java、Go、C++ 等多種 SDK。
6. 云原生架構(gòu): 支持 Kubernetes 部署,便于云上運行。
Milvus 的應(yīng)用場景
1. 圖像和視頻檢索(內(nèi)容推薦)
2. 自然語言處理(語義檢索與推薦)
3. 推薦系統(tǒng)(個性化推薦)
4. 生物醫(yī)學(xué)數(shù)據(jù)分析(DNA 比對)
5. 安全監(jiān)控(面部識別)
Milvus 快速上手教程
1. 環(huán)境準(zhǔn)備
? 操作系統(tǒng):Linux/macOS/Windows
? 安裝 Docker(推薦)或 Kubernetes(用于生產(chǎn)環(huán)境)
2. 安裝 Milvus
使用 Docker 快速啟動:
docker pull milvusdb/milvus:latest
docker run -d –name milvus-standalone -p 19530:19530 -p 8080:8080 milvusdb/milvus:latest
3. 創(chuàng)建 Milvus 客戶端
安裝 Milvus Python SDK:
pip install pymilvus
4. 連接到 Milvus
from pymilvus import connections
connections.connect(
alias=”default”,
host=”localhost”,
port=”19530″
)
5. 創(chuàng)建集合與插入數(shù)據(jù)
from pymilvus import Collection, FieldSchema, CollectionSchema, DataType
# 定義字段
fields = [
FieldSchema(name=”id”, dtype=DataType.INT64, is_primary=True, auto_id=True),
FieldSchema(name=”embedding”, dtype=DataType.FLOAT_VECTOR, dim=128)
]
# 定義集合架構(gòu)
schema = CollectionSchema(fields, “向量數(shù)據(jù)集合”)
# 創(chuàng)建集合
collection = Collection(“example_collection”, schema)
# 插入數(shù)據(jù)
import numpy as np
data = [
[i for i in range(1000)], # id
np.random.random([1000, 128]).tolist() # 隨機向量
]
collection.insert(data)
6. 創(chuàng)建索引與檢索
# 創(chuàng)建索引
index_params = {
“metric_type”: “L2”,
“index_type”: “IVF_FLAT”,
“params”: {“nlist”: 100}
}
collection.create_index(field_name=”embedding”, index_params=index_params)
# 搜索向量
search_params = {
“metric_type”: “L2”,
“params”: {“nprobe”: 10}
}
query_vector = np.random.random([1, 128]).tolist()
results = collection.search(
data=query_vector,
anns_field=”embedding”,
param=search_params,
limit=5
)
# 輸出結(jié)果
for result in results[0]:
print(f”ID: {result.id}, Distance: {result.distance}”)
Milvus 官方資源
? 官網(wǎng):Milvus 官方網(wǎng)站
? 文檔:Milvus 文檔中心
? GitHub:Milvus GitHub 倉庫
如果需要更詳細的教程或針對特定場景的使用指導(dǎo),請告訴我!
]]>1. langdetect
? 簡介: langdetect 是一個非常流行的語言檢測庫,基于 Google 的 language-detection 項目。它可以檢測多種語言,并且對于短文本也有不錯的識別效果。
? 安裝:
pip install langdetect
? 使用示例:
from langdetect import detect
text = “Bonjour tout le monde”
language = detect(text)
print(language) # 輸出: ‘fr’ (法語)
2. langid
? 簡介: langid 是另一個非常強大的語言識別庫,支持97種語言。它的特點是完全自包含且無需外部依賴。
? 安裝:
pip install langid
? 使用示例:
import langid
text = “Hola, ?cómo estás?”
language, _ = langid.classify(text)
print(language) # 輸出: ‘es’ (西班牙語)
3. polyglot
? 簡介: polyglot 是一個支持多語言處理的庫,它不僅提供語言識別功能,還支持情感分析、實體識別等多種自然語言處理任務(wù)。
? 安裝:
pip install polyglot
? 使用示例:
from polyglot.detect import Detector
text = “Ceci est un exemple de texte en fran?ais”
detector = Detector(text)
language = detector.language.code
print(language) # 輸出: ‘fr’ (法語)
4. TextBlob
? 簡介: TextBlob 是一個簡潔易用的自然語言處理工具包,雖然它主要用于情感分析、詞性標(biāo)注等任務(wù),但也支持語言識別。
? 安裝:
pip install textblob
? 使用示例:
from textblob import TextBlob
text = “Hello, how are you?”
blob = TextBlob(text)
print(blob.detect_language()) # 輸出: ‘en’ (英語)

5. FastText (by Facebook)
? 簡介: FastText 是一個由 Facebook 提供的開源庫,除了高效的詞向量表示外,它也能很好地進行語言識別。它支持多達170多種語言。
? 安裝:
pip install fasttext
? 使用示例:
import fasttext
model = fasttext.load_model(‘lid.176.bin’) # 下載預(yù)訓(xùn)練模型
text = “Ceci est un texte en fran?ais”
prediction = model.predict(text)
print(prediction) # 輸出: (‘__label__fr’,)
6. cld3 (Compact Language Detector v3)
? 簡介: cld3 是一個高效的語言檢測庫,基于 Google 的 Compact Language Detector v3。它對短文本和多語言文本都有不錯的支持。
? 安裝:
pip install cld3
? 使用示例:
import cld3
text = “Hola, ?cómo estás?”
language = cld3.get_language(text)
print(language) # 輸出: Language: es (西班牙語)
總結(jié):
? 如果需要一個簡單、易用的工具,langdetect 和 langid 都是不錯的選擇。
? 如果對處理多語言的文本和需要其他 NLP 功能有需求,可以考慮使用 polyglot 或 TextBlob。
? 如果需要更高精度的檢測,尤其是在短文本的情況下,F(xiàn)astText 和 cld3 是更強大的選擇。
你可以根據(jù)具體需求選擇適合的工具!
]]>1. 工具介紹
? Pymupdf4llm
是基于 PyMuPDF 的輕量級庫,用于解析 PDF 文檔并將其輸出為適合 LLM 使用的格式。主要側(cè)重文本提取和結(jié)構(gòu)化處理,適合生成上下文良好的段落,便于用于 LLM 的問答場景。
? pdf-extract-api
是一個基于 API 的工具,專注于從 PDF 中提取特定的數(shù)據(jù)(如表格、元數(shù)據(jù)、關(guān)鍵段落等)。它通常提供更精細的配置選項,且需要在線服務(wù)支持。
2. 優(yōu)點
Pymupdf4llm
? 開源和輕量化:基于 PyMuPDF,依賴簡單,不需要網(wǎng)絡(luò)請求。
? 靈活性:支持本地化部署和定制,適合對隱私敏感的數(shù)據(jù)處理。
? LLM優(yōu)化:文本提取經(jīng)過優(yōu)化,更適合直接喂給 LLM 使用。
? 社區(qū)支持:有 Python 社區(qū)的廣泛支持,文檔豐富。
pdf-extract-api
? 精確提取:通過 API 提供強大的功能,如識別表格、圖像提取以及結(jié)構(gòu)化內(nèi)容分離。
? 便捷性:通常不需要用戶過多了解 PDF 內(nèi)部結(jié)構(gòu),適合快速實現(xiàn)提取目標(biāo)。
? 擴展性:可與其他 API 組合實現(xiàn)復(fù)雜任務(wù),如 OCR 集成處理掃描 PDF。
3. 缺點
Pymupdf4llm
? 復(fù)雜性有限:對非常復(fù)雜的 PDF(如多層嵌套、表格、圖片)支持不如專業(yè)化工具。
? 手動調(diào)整需求高:對提取后的數(shù)據(jù),需要編寫代碼進一步清洗和整理。
pdf-extract-api
? 依賴在線服務(wù):需要網(wǎng)絡(luò)訪問,可能對敏感文檔不適合。
? 成本問題:通常是收費服務(wù),使用量大時費用可能較高。
? 上手門檻高:需要了解 API 調(diào)用的基礎(chǔ),復(fù)雜設(shè)置可能增加學(xué)習(xí)成本。
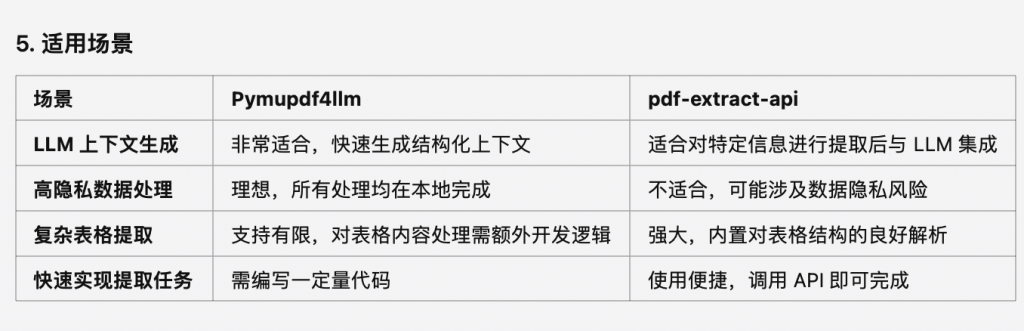
4. 準(zhǔn)備度與上手難度
指標(biāo) Pymupdf4llm pdf-extract-api
部署與安裝 安裝簡單(pip install pymupdf 等) 需要注冊 API 服務(wù)并配置訪問權(quán)限
學(xué)習(xí)曲線 易于上手,Python 開發(fā)者友好 需要熟悉 API 文檔,配置參數(shù)稍復(fù)雜
定制化能力 高,代碼靈活,自由控制輸出內(nèi)容和格式 中,定制需依賴 API 提供的接口和選項
速度 本地運行,速度快 API 請求受網(wǎng)絡(luò)和服務(wù)端性能影響
環(huán)境依賴 本地運行,無需聯(lián)網(wǎng) 需聯(lián)網(wǎng)使用在線 API 服務(wù)
總結(jié)與建議
? 選擇 Pymupdf4llm:
如果你希望完全掌控 PDF 的提取邏輯、對敏感數(shù)據(jù)有隱私保護需求,并傾向于本地化輕量部署,Pymupdf4llm 是不錯的選擇。
? 選擇 pdf-extract-api:
如果需要快速處理復(fù)雜的 PDF 任務(wù)(如表格解析、精確提取特定內(nèi)容),且不介意使用在線服務(wù)和支付一定費用,那么 pdf-extract-api 更加適合。
最終選擇取決于項目的復(fù)雜性、隱私要求和開發(fā)資源。
]]>RAGFlow 是一個基于對文檔的深入理解的開源 RAG(檢索增強生成)引擎。它為任何規(guī)模的企業(yè)提供了簡化的 RAG 工作流程,結(jié)合了 LLM(大型語言模型)以提供真實的問答功能,并以來自各種復(fù)雜格式數(shù)據(jù)的有根據(jù)的引文為后盾。
demo鏈接:RAGFlow
特點:
1、有一定的數(shù)據(jù)質(zhì)量保證,能從復(fù)雜的非結(jié)構(gòu)化數(shù)據(jù)中提取基于文檔理解的深度知識。
2、內(nèi)置模板,可以基于模板形成知識庫;文檔分塊可以實現(xiàn)人工干預(yù),提高文檔質(zhì)量;
3、可以兼容異構(gòu)數(shù)據(jù)源,支持 Word、幻燈片、excel、txt、圖像、掃描副本、結(jié)構(gòu)化數(shù)據(jù)、網(wǎng)頁等。
4、 自動化且輕松的 RAG 工作流程
- 簡化的 RAG 編排同時滿足了個人和大型企業(yè)的需求。
- 可配置的 LLM 以及嵌入模型。
- 多重召回與融合的重新排名配對。
- 直觀的 API,可與業(yè)務(wù)無縫集成。
RAGFlow架構(gòu)圖
部署要求:
- CPU >= 4 cores
- RAM >= 16 GB
- Disk >= 50 GB
- Docker >= 24.0.0 & Docker Compose >= v2.26.1
啟動 服務(wù)器
- 確保 >= 262144:
vm.max_map_count要檢查 的值 :vm.max_map_count$ sysctl vm.max_map_count如果不是,則重置為至少 262144 的值。vm.max_map_count
- # In this case, we set it to 262144:$ sudo sysctl -w vm.max_map_count=262144此更改將在系統(tǒng)重啟后重置。為了確保您的更改保持永久,請相應(yīng)地在?/etc/sysctl.conf?中添加或更新該值:
vm.max_map_count - vm.max_map_count=262144
- 克隆存儲庫:$ git clone https://github.com/infiniflow/ragflow.git構(gòu)建預(yù)構(gòu)建的 Docker 鏡像并啟動服務(wù)器:
- 以下命令下載 RAGFlow slim () 的開發(fā)版本 Docker 映像。請注意,RAGFlow slim Docker 映像不包括嵌入模型或 Python 庫,因此大小約為 1GB。
dev-slim$ cd ragflow/docker$ docker compose -f docker-compose.yml up -d注意:包含嵌入模型和 Python 庫的 RAGFlow Docker 映像的大小約為 9GB,加載時間可能要長得多。- 要下載特定版本的 RAGFlow slim Docker 鏡像,請將?docker/.env?中的變量更新為所需版本。例如。進行此更改后,請重新運行上述命令以啟動下載。
RAGFlow_IMAGERAGFLOW_IMAGE=infiniflow/ragflow:v0.12.0-slim - 要下載 RAGFlow Docker 映像的開發(fā)版本(包括嵌入模型和 Python 庫),請將?docker/.env?中的變量更新為 。進行此更改后,請重新運行上述命令以啟動下載。
RAGFlow_IMAGERAGFLOW_IMAGE=infiniflow/ragflow:dev - 要下載特定版本的 RAGFlow Docker 映像(包括嵌入模型和 Python 庫),請將?docker/.env?中的變量更新為所需的版本。例如。進行此更改后,請重新運行上述命令以啟動下載。
RAGFlow_IMAGERAGFLOW_IMAGE=infiniflow/ragflow:v0.12.0
- 要下載特定版本的 RAGFlow slim Docker 鏡像,請將?docker/.env?中的變量更新為所需版本。例如。進行此更改后,請重新運行上述命令以啟動下載。
- 在服務(wù)器啟動并運行后檢查服務(wù)器狀態(tài):$ docker logs -f ragflow-server以下輸出確認系統(tǒng)已成功啟動:
- ____ ___ ______ ______ __
/ __ \ / | / ____// ____// /____ _ __
/ /_/ // /| | / / __ / /_ / // __ \| | /| / /
/ _, _// ___ |/ /_/ // __/ / // /_/ /| |/ |/ /
/_/ |_|/_/ |_|\____//_/ /_/ \____/ |__/|__/
* Running on all addresses (0.0.0.0)
* Running on http://127.0.0.1:9380
* Running on http://x.x.x.x:9380 INFO:werkzeug:Press CTRL+C to quit如果您跳過此確認步驟并直接登錄 RAGFlow,您的瀏覽器可能會提示錯誤,因為此時您的 RAGFlow 可能沒有完全初始化。network abnormal
- 在您的 Web 瀏覽器中,輸入服務(wù)器的 IP 地址并登錄 RAGFlow。使用默認設(shè)置時,您只需輸入 (sans?port number) 作為使用默認配置時可以省略默認 HTTP 服務(wù)端口。
http://IP_OF_YOUR_MACHINE80 - 在 service_conf.yaml 中,選擇所需的 LLM 工廠,并使用相應(yīng)的 API 密鑰更新字段。
user_default_llmAPI_KEY有關(guān)更多信息,請參閱 llm_api_key_setup。
部署完成后,還需要對RAGFlow進行配置,需要關(guān)注以下幾點:
- .env:保留系統(tǒng)的基本設(shè)置,例如
SVR_HTTP_PORTMYSQL_PASSWORDMINIO_PASSWORD - service_conf.yaml:配置后端服務(wù)。
- docker-compose.yml:系統(tǒng)依賴 docker-compose.yml 啟動。
您必須確保對 .env 文件的更改與 service_conf.yaml 文件中的更改一致。
./docker/README 文件提供了環(huán)境設(shè)置和服務(wù)配置的詳細描述,您需要確保 ./docker/README 文件中列出的所有環(huán)境設(shè)置都與 service_conf.yaml 文件中的相應(yīng)配置保持一致。
要更新默認 HTTP 服務(wù)端口 (80),請轉(zhuǎn)到 docker-compose.yml 并更改為 。80:80<YOUR_SERVING_PORT>:80
對上述配置的更新需要重啟所有容器才能生效:
$ docker compose -f docker/docker-compose.yml up -d
 在不嵌入模型的情況下構(gòu)建 Docker 鏡像
在不嵌入模型的情況下構(gòu)建 Docker 鏡像
此映像的大小約為 1 GB,依賴于外部 LLM 和嵌入服務(wù)。
git clone https://github.com/infiniflow/ragflow.git
cd ragflow/
pip3 install huggingface-hub nltk
python3 download_deps.py
docker build -f Dockerfile.slim -t infiniflow/ragflow:dev-slim .
 構(gòu)建包含嵌入模型的 Docker 鏡像
構(gòu)建包含嵌入模型的 Docker 鏡像
此映像的大小約為 9 GB。由于它包括嵌入模型,因此它僅依賴于外部 LLM 服務(wù)。
git clone https://github.com/infiniflow/ragflow.git
cd ragflow/
pip3 install huggingface-hub nltk
python3 download_deps.py
docker build -f Dockerfile -t infiniflow/ragflow:dev .
 從源頭啟動服務(wù)進行開發(fā)
從源頭啟動服務(wù)進行開發(fā)
- 安裝 Poetry,如果已安裝,請?zhí)^此步驟:curl -sSL https://install.python-poetry.org | python3 –
- 克隆源碼并安裝 Python 依賴項:git clone https://github.com/infiniflow/ragflow.git
cd ragflow/
export POETRY_VIRTUALENVS_CREATE=true POETRY_VIRTUALENVS_IN_PROJECT=true
~/.local/bin/poetry install –sync –no-root # install RAGFlow dependent python modules - 使用 Docker Compose 啟動依賴服務(wù)(MinIO、Elasticsearch、Redis 和 MySQL):docker compose -f docker/docker-compose-base.yml up -d
- 添加以下行以將?docker/service_conf.yaml?中指定的所有主機解析為:
/etc/hosts127.0.0.1
127.0.0.1 es01 mysql minio redis- 在?docker/service_conf.yaml?中,將 mysql 端口更新為 ,將 es 端口更新為?,如 docker/.env?中指定。
54551200
- 如果無法訪問 HuggingFace,請將環(huán)境變量設(shè)置為使用鏡像站點:
HF_ENDPOINTexport HF_ENDPOINT=https://hf-mirror.com啟動 backend service: - source .venv/bin/activate
export PYTHONPATH=$(pwd)bash docker/launch_backend_service.sh - 安裝前端依賴項:
- cd webnpm install –force
- 將前端配置為在?.umirc.ts?更新為:
proxy.targethttp://127.0.0.1:9380
啟動前端服務(wù):
npm run dev 以下輸出確認系統(tǒng)已成功啟動完成。
1、Text2KG 的使用
Text2KG是一個開源項目,能夠利用大型語言模型(zero-shot)跨領(lǐng)域從文本中提取實體和關(guān)系,自動構(gòu)建和更新知識圖譜,并通過Neo4j進行可視化。
iText2KG由四個主要模塊組成:文檔提取器、增量實體提取器、增量關(guān)系提取器、圖形集成器和可視化。它們協(xié)同工作,從非結(jié)構(gòu)化文本構(gòu)建和可視化知識圖譜。
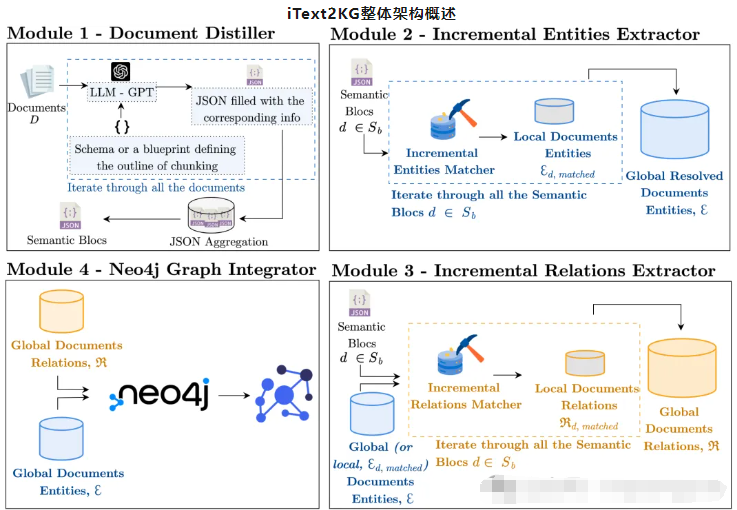
- 文檔提取器(Document Distiller):該模塊處理原始文檔,并根據(jù)用戶定義的模式將其重新表述為語義塊。它通過關(guān)注相關(guān)信息并以預(yù)定義的格式對其進行結(jié)構(gòu)化來提高信噪比。
- 增量實體提取器(Incremental Entity Extractor):此模塊從語義塊中提取唯一實體并解決歧義以確保每個實體都有明確定義。它使用余弦相似度度量將局部實體與全局實體進行匹配。
- 增量關(guān)系提取器(Incremental Relation Extractor):此模塊識別提取實體之間的關(guān)系。它可以以兩種模式運行:使用全局實體豐富圖形中的潛在信息,或使用局部實體建立更精確的關(guān)系。
- 圖形集成器和可視化(Graph Integrator and Visualization):此模塊將提取的實體和關(guān)系集成到 Neo4j 數(shù)據(jù)庫中,提供知識圖譜的可視化表示。它允許對結(jié)構(gòu)化數(shù)據(jù)進行交互式探索和分析。
四個模塊中,增量實體提取器與增量關(guān)系提取器最為關(guān)鍵,采用大模型來實現(xiàn),LLM提取代表一個唯一概念的實體,以避免語義混合的實體。顯示了使用 Langchain JSON 解析器的實體和關(guān)系提取prompt。分類如下:藍色 – 由 Langchain 自動格式化的prompt;常規(guī) – iText2KG設(shè)計的prompt;斜體 – 專門為實體和關(guān)系提取設(shè)計的prompt。(a)關(guān)系提取prompt和(b)實體提取prompt。

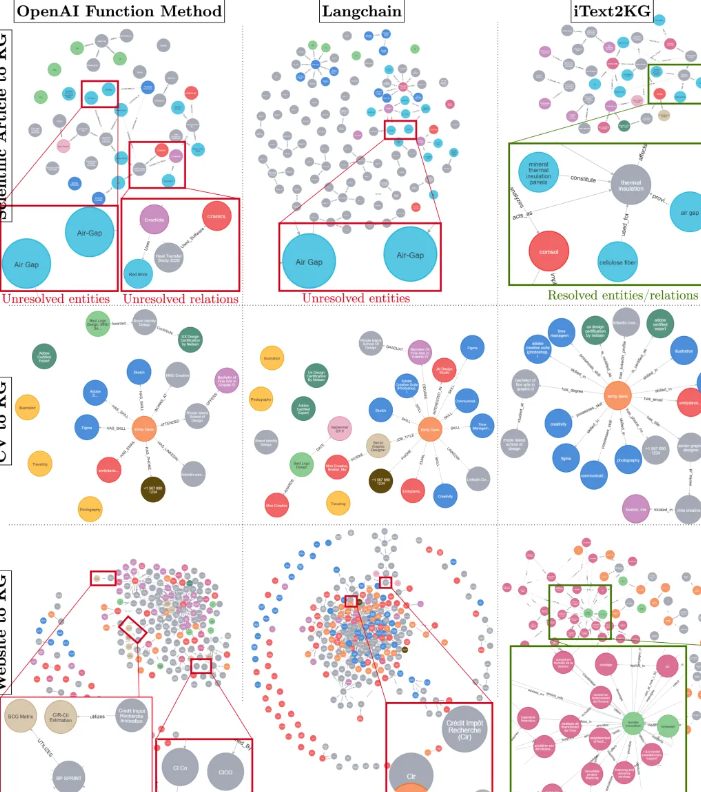
為了說明知識圖譜構(gòu)建的結(jié)果,在三種不同場景下,將基線方法與iText2KG進行了比較:
- 基線方法在所有三種知識圖譜構(gòu)建場景中都揭示了存在沒有關(guān)系的孤立節(jié)點。這種現(xiàn)象可能歸因于實體提取和關(guān)系提取的同時執(zhí)行,這可能會在語言模型中引起幻覺效應(yīng),導(dǎo)致“遺忘”效應(yīng),即分離實體和關(guān)系提取的過程可以提高性能。
- 在“網(wǎng)站到知識圖譜”的場景中,輸入文檔數(shù)量的增加與圖中噪聲節(jié)點的出現(xiàn)有關(guān)。這強調(diào)了對文檔進行有效精煉和蒸餾的模塊1的關(guān)鍵需求。
- iText2KG方法在三種知識圖譜構(gòu)建場景中展示了改進的實體和關(guān)系解析能力。當(dāng)輸入文檔較少且由簡單、非復(fù)雜短語組成時,語言模型在實體和關(guān)系解析方面表現(xiàn)出高效率,如“簡歷到知識圖譜”過程中所證明的。相反,隨著數(shù)據(jù)集變得更加復(fù)雜和龐大,挑戰(zhàn)也隨之增加,如“網(wǎng)站到知識圖譜”場景所示。此外,重要的是要強調(diào)輸入文檔的分塊大小和閾值對知識圖譜構(gòu)建的影響。文檔分餾器的輸入文檔可以是獨立的文檔或分塊。如果分塊大小較小,則語義塊將從文檔中捕獲更具體的詳細信息,反之亦然
一種由 LLM 驅(qū)動的零樣本方法,使用大型語言模型構(gòu)建增量知識圖譜(KG)
iText2KG 是一個 Python 包,通過利用大型語言模型從文本文檔中提取實體和關(guān)系,逐步構(gòu)建具有已解析實體和關(guān)系的一致知識圖譜。
它具有零樣本能力,無需專門的訓(xùn)練即可跨各個領(lǐng)域提取知識。
它包含四個模塊:文檔提煉器、增量實體提取器、增量關(guān)系提取器和圖形集成器與可視化。
- 文檔提取器:此模塊將原始文檔重新表述為預(yù)定義的語義塊,并由指導(dǎo) LLM 提取特定信息的模式引導(dǎo)。
- 增量實體提取器:此模塊識別并解析語義塊內(nèi)的唯一語義實體,確保實體之間的清晰度和區(qū)別。
- 增量關(guān)系提取器:此組件處理已解析的實體以檢測語義上唯一的關(guān)系,解決語義重復(fù)的挑戰(zhàn)。
Neo4j?圖形集成器:最后一個模塊以圖形格式可視化關(guān)系和實體,利用 Neo4j 進行有效表示。
對于我們的 iText2KG 它包含了兩大特點
- 增量構(gòu)建:
iText2KG?允許增量構(gòu)建?KG,這意味著它可以在新數(shù)據(jù)可用時不斷更新和擴展圖,而無需進行大量重新處理。 - 零樣本學(xué)習(xí):該框架利用?
LLM?的零樣本功能,使其無需預(yù)定義集或外部本體即可運行。這種靈活性使其能夠適應(yīng)各種?KG?構(gòu)建場景,而無需進行大量訓(xùn)練或微調(diào)。
一 、設(shè)置模型
在運行 iText2KG 之前,我們先設(shè)置好大模型,我這里選擇的是 OpenAi 的模型以及 HuggingFace 的 bge-large-zh embedding 模型。這么選擇也是考慮到構(gòu)建 KG 的準(zhǔn)確度。
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI, OpenAIEmbeddings
import os
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "*****"
openai_api_key = os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"]
openai_llm_model = llm = ChatOpenAI(
model="gpt-4o-mini",
temperature=0,
max_tokens=None,
timeout=None,
max_retries=2,
)
messages = [
(
"system",
"You are a helpful assistant that translates English to French. Translate the user sentence.",
),
("human", "I love programming."),
]
ai_msg=openai_llm_model.invoke(messages)開始部署我們的 Embedding 模型:
from langchain_huggingface.embeddings import HuggingFaceEmbeddings
openai_embeddings_model = HuggingFaceEmbeddings(model_name="BAAI/bge-large-zh-v1.5")
text = "This is a test document."
query_result = openai_embeddings_model.embed_query(text)
query_result[:3]
doc_result = openai_embeddings_model.embed_documents([text])二 、使用 iText2KG 構(gòu)建 KG
我們這里的場景是,給出一篇簡歷,使用知識圖譜將在線職位描述與生成的簡歷聯(lián)系起來。
設(shè)定目標(biāo)是評估候選人是否適合這份工作。
我們可以為 iText2KG 的每個模塊使用不同的 LLM 或嵌入模型。但是,重要的是確保節(jié)點和關(guān)系嵌入的維度在各個模型之間保持一致。
如果嵌入維度不同,余弦相似度可能難以準(zhǔn)確測量向量距離以進行進一步匹配。
我們的簡歷放到根目錄,加載簡歷:
from langchain.document_loaders import PyPDFLoader
loader = PyPDFLoader(f"./CV_Emily_Davis.pdf")
pages = loader.load_and_split()初始化 DocumentDistiller 引入 llm :
from itext2kg.documents_distiller import DocumentsDisiller, CV
document_distiller = DocumentsDisiller(llm_model = openai_llm_model)信息提煉:
IE_query = '''
# DIRECTIVES :
- Act like an experienced information extractor.
- You have a chunk of a CV.
- If you do not find the right information, keep its place empty.
'''
# 使用定義好的查詢和輸出數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu)提煉文檔。
distilled_cv = document_distiller.distill(documents=[page.page_content.replace("{", '[').replace("}", "]") for page in pages], IE_query=IE_query, output_data_structure=CV)將提煉后的文檔格式化為語義部分。
semantic_blocks_cv = [f"{key} - {value}".replace("{", "[").replace("}", "]") for key, value in distilled_cv.items() if value !=[] and value != "" and value != None]我們可以自定義輸出數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu),我們這里定義了4種,工作經(jīng)歷模型,崗位,技能,證書。
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
from typing import List, Optional
class JobResponsibility(BaseModel):
description: str = Field(..., description="A specific responsibility in the job role")
class JobQualification(BaseModel):
skill: str = Field(..., description="A required or preferred skill for the job")
class JobCertification(BaseModel):
certification: str = Field(..., description="Required or preferred certifications for the job")
class JobOffer(BaseModel):
job_offer_title: str = Field(..., description="The job title")
company: str = Field(..., description="The name of the company offering the job")
location: str = Field(..., description="The job location (can specify if remote/hybrid)")
job_type: str = Field(..., description="Type of job (e.g., full-time, part-time, contract)")
responsibilities: List[JobResponsibility] = Field(..., description="List of key responsibilities")
qualifications: List[JobQualification] = Field(..., description="List of required or preferred qualifications")
certifications: Optional[List[JobCertification]] = Field(None, description="Required or preferred certifications")
benefits: Optional[List[str]] = Field(None, description="List of job benefits")
experience_required: str = Field(..., description="Required years of experience")
salary_range: Optional[str] = Field(None, description="Salary range for the position")
apply_url: Optional[str] = Field(None, description="URL to apply for the job")定義一個招聘工作需求的描述:
job_offer = """
About the Job Offer
THE FICTITIOUS COMPANY
FICTITIOUS COMPANY is a high-end French fashion brand known for its graphic and poetic style, driven by the values of authenticity and transparency upheld by its creator Simon Porte Jacquemus.
Your Role
Craft visual stories that captivate, inform, and inspire. Transform concepts and ideas into visual representations. As a member of the studio, in collaboration with the designers and under the direction of the Creative Designer, you should be able to take written or spoken ideas and convert them into designs that resonate. You need to have a deep understanding of the brand image and DNA, being able to find the style and layout suited to each project.
Your Missions
Translate creative direction into high-quality silhouettes using Photoshop
Work on a wide range of projects to visualize and develop graphic designs that meet each brief
Work independently as well as in collaboration with the studio team to meet deadlines, potentially handling five or more projects simultaneously
Develop color schemes and renderings in Photoshop, categorized by themes, subjects, etc.
Your Profile
Bachelor’s degree (Bac+3/5) in Graphic Design or Art
3 years of experience in similar roles within a luxury brand's studio
Proficiency in Adobe Suite, including Illustrator, InDesign, Photoshop
Excellent communication and presentation skills
Strong organizational and time management skills to meet deadlines in a fast-paced environment
Good understanding of the design process
Freelance cont繼續(xù)使用上面方法做信息提煉:
IE_query = '''
# DIRECTIVES :
- Act like an experienced information extractor.
- You have a chunk of a job offer description.
- If you do not find the right information, keep its place empty.
'''
distilled_Job_Offer = document_distiller.distill(documents=[job_offer], IE_query=IE_query, output_data_structure=JobOffer)
print(distilled_Job_Offer)
semantic_blocks_job_offer = [f"{key} - {value}".replace("{", "[").replace("}", "]") for key, value in distilled_Job_Offer.items() if value !=[] and value != "" and value != None]到這里準(zhǔn)備工作完成,簡歷和工作需求都已經(jīng)提煉完畢,然后正式開始構(gòu)建 graph,我們將簡歷的所有語義塊作為一個塊傳遞給了 LLM。
也將工作需求作為另一個語義塊傳遞,也可以在構(gòu)建圖時將語義塊分開。
我們需要注意每個塊中包含多少信息,然后好將它與其他塊連接起來,我們在這里做的就是一次性傳遞所有語義塊。
from itext2kg import iText2KG
itext2kg = iText2KG(llm_model = openai_llm_model, embeddings_model = openai_embeddings_model)
global_ent, global_rel = itext2kg.build_graph(sections=[semantic_blocks_cv], ent_threshold=0.6, rel_threshold=0.6)
global_ent_, global_rel_ = itext2kg.build_graph(sections=[semantic_blocks_job_offer], existing_global_entities = global_ent, existing_global_relationships = global_rel, ent_threshold=0.6, rel_threshold=0.6)iText2KG 構(gòu)建 KG 的過程我們看到有很多參數(shù),下面分貝是對每個參數(shù)的表示做一些解釋:
llm_model:用于從文本中提取實體和關(guān)系的語言模型實例。embeddings_model:用于創(chuàng)建提取實體的向量表示的嵌入模型實例。sleep_time (int):遇到速率限制或錯誤時等待的時間(以秒為單位)(僅適用于?OpenAI)。默認為 5 秒。
iText2KG 的 build_graph 參數(shù):
sections?(List[str]):字符串(語義塊)列表,其中每個字符串代表文檔的一部分,將從中提取實體和關(guān)系。existing_global_entities?(List[dict], optional):與新提取的實體進行匹配的現(xiàn)有全局實體列表。每個實體都表示為一個字典。existing_global_relationships (List[dict], optional):與新提取的關(guān)系匹配的現(xiàn)有全局關(guān)系列表。每個關(guān)系都表示為一個字典。ent_threshold (float, optional):實體匹配的閾值,用于合并不同部分的實體。默認值為 0.7。rel_threshold (float, optional):關(guān)系匹配的閾值,用于合并不同部分的關(guān)系。默認值為 0.7。
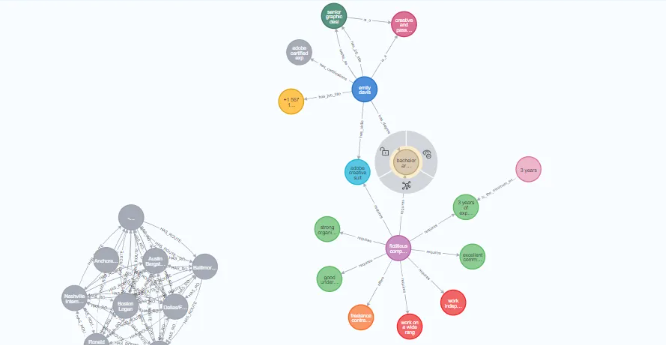
從圖中結(jié)果看到我們構(gòu)建過程中的實體,和關(guān)聯(lián)關(guān)系。
最后使用 GraphIntegrator 對構(gòu)建的知識圖譜進行可視化。
使用指定的憑據(jù)訪問圖形數(shù)據(jù)庫 Neo4j,并對生成的圖形進行可視化,以提供從文檔中提取的關(guān)系和實體的視覺表示。
from itext2kg.graph_integration import GraphIntegrator
URI = "bolt://3.216.93.32:7687"
USERNAME = "neo4j"
PASSWORD = "selection-cosal-cubes"
new_graph = {}
new_graph["nodes"] = global_ent_
new_graph["relationships"] = global_rel_
GraphIntegrator(uri=URI, username=USERNAME, password=PASSWORD).visualize_graph(json_graph=new_graph)打開我們的 Neo4j 圖形數(shù)據(jù)庫: